01. What is the primary function of segmentation in network management?
a) To encrypt data traffic across the network
b) To connect multiple physical switches in a single logical interface
c) To divide a network into smaller, isolated segments for enhanced security
d) To enhance the decryption and encryption speeds within the network
02. One firewall policy in an enterprise firewall is essentially used for IPS. Which configuration must the administrator check in this firewall policy to validate optimum performance for IPS?
a) set cp-accel-mode enable
b) set inspection-mode proxy
c) set offload enable
d) set np-acceleration enable
03. An administrator configured FGSP cluster members to encrypt the session synchronization. When the administrator takes a sniffer trace on the dedicated interface for the synchronization, the sniffer trace shows UDP packets only.
Which two reasons could cause the sniffer to capture only UDP packets?
(Choose two.)
a) The administration has not configured the SESSYNC_1 tunnel.
b) encryption is not set to enable on both members.
c) The psksecret value does not match.
d) The encryption is encapsulated in UDP packets.
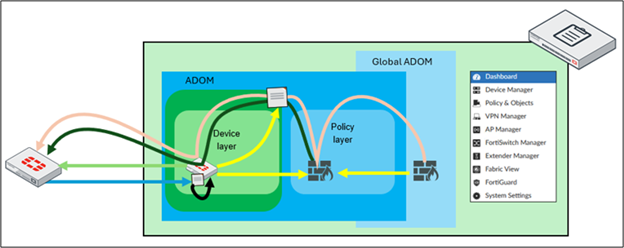
04. Refer to the exhibit, which shows the device and policy layers for FortiGate key operations.
How can the administrator restore a previous FortiGate configuration, which had more policies than the current one, without the layer synchronization between the device and policy layers on FortiManager?
a) Locate the configuration ID in the FortiGate revision history, click revert, install the device settings, and import policies to sync the policy package.
b) Use the global ADOM to access the previous configurations and install policies on ADOM devices to synchronize all layers.
c) Find the configuration file by date and time in the provisioning templates, then reinstall the policy package to apply the configuration changes.
d) Retrieve the configuration, import system templates, and reinstall the policy package on FortiGate.
05. An administrator must automate a weekly backup of all the FortiGate devices in an enterprise network. Which two steps must the administrator follow to implement this?
(Choose two.)
a) Integrate all the FortiGate devices in a Security Fabric environment.
b) Create a script to be run in the device database.
c) Create metadata variables for all the FortiGate devices.
d) Create an automation stitch.
06. What are two impacts on applications if adjusting the TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS) on FortiGate?
(Choose two.)
a) The MSS configuration is prone to errors since it requires a thorough understanding of the network path.
b) The packet count increases adding unnecessary TCP headers when the MSS value is increased.
c) The overall data throughput is decreased when there is a decrease in MSS value.
d) The network efficiency improves when there is a decrease in MSS value.
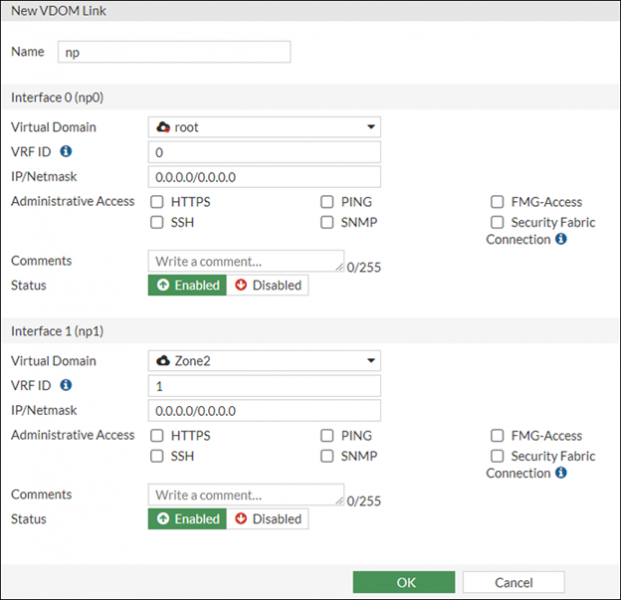
07. Refer to the exhibit, which shows VDOM link interfaces.
For the VDOM link shown, what is the meaning of np0 and np1?
a) They are the VRD ID numbers of each VDOM interface.
b) FortiGate automatically assigns a native ASIC network processor to available VDOM interfaces.
c) They represent the ID number of each VDOM for traffic management.
d) FortiGate automatically assigns unique names to VDOM links by appending 0 and 1.
08. An administrator wants to simplify a new hub-and-spoke network deployment with the BGP recommended configuration. Which two sections on FortiManager must the administrator use?
(Choose two.)
a) Provisioning Templates
b) Meta Fields
c) Metadata Variables
d) Automation Stitch
09. What does hyperscale capability in data center firewalls typically support?
a) Application layer operations such as intrusion prevention
b) Network speeds ranging from 10 Gbps to 1000 Gbps
c) Enhanced encryption and decryption processes only
d) Bundling of multiple physical interfaces for a single logical interface
10. An administrator must ensure that users cannot access sites containing malware and spyware, while also protecting them from phishing attempts. What is the most resource-efficient method to block access to these sites?
a) Set up a DNS filter and block domains related to these categories to stop users from reaching malicious content.
b) Create a custom IPS policy to monitor and block all outbound traffic related to malware, spyware, and phishing sites.
c) Configure FortiGuard Web Filtering and block the categories malware, spyware, and phishing to prevent access to such sites.
d) Enable antivirus profiles to scan all web traffic and block downloads from these malicious sites.
 Before you write the Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Administrator (FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4) certification exam, you may have certain doubts in your mind regarding the pattern of the test, the types of questions asked in it, the difficulty level of the questions and time required to complete the questions. These Fortinet Certified Solution Specialist - Network Security (Enterprise Firewall Administrator) sample questions and demo exam help you in removing these doubts and prepare you to take the test.
Before you write the Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Administrator (FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4) certification exam, you may have certain doubts in your mind regarding the pattern of the test, the types of questions asked in it, the difficulty level of the questions and time required to complete the questions. These Fortinet Certified Solution Specialist - Network Security (Enterprise Firewall Administrator) sample questions and demo exam help you in removing these doubts and prepare you to take the test.